Bialystok Tall Tower (BIK)
Bialystok, Poland
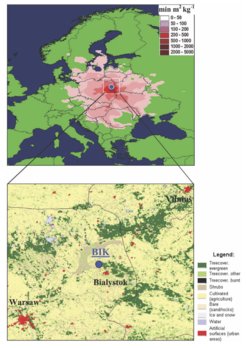
The Bialystok tall tower (53 13 N, 23 01 E, 183 m a.s.l.) was set up in 2002 as part of the EC-funded CHIOTTO (Continuous HIgh-precisiOn Tall Tower Observations of Greenhouse Gases in Europe, EVK2-CT-2002-00163) and became operational in August 2005. The observatory is registered under the GAW-ID BIK and the WMO-ID 12295-0, and operates up to present-day. Early 2024, the BIK tall tower has been transferred to the University of Krakow, for more info see here, and is now jointly operated by AHG and the MPI-BGC.
The BIK tall tower was set up at a pre-existing television tower owned by TP EmiTel in Eastern Poland. BIK is classified as rural background site because of its low population in the neighbouring area. The land is mostly covered by crops and grasslands, with patches of forest and wetlands. The nearest town, Bialystok, with about 300 000 inhabitants, is situated about 20 km SE of the tower; the metropolitan area of Warsaw lies more than 160 km SW of the tower. The foot-print area (see figure) within a few hundreds of kilometres around the tower is flat, with an elevation above sea level of about 150 m, and covers a large part of Eastern Central Europe. It is therefore an important station to constrain the European carbon balance as it measures the atmospheric concentrations transported eastwards from Central Europe.
The system measures air sampled from five heights of the tower, between 5 and 300 m above ground, where quasi-continuous measurements of CO2, CH4 and N2O are performed. Since then, the station has also been part of the MPI-BGC flask network, which provides roughly bi-weekly air samples of the mixing ratios of CO2, CO, CH4, N2O, H2 and SF6. In addition, measurements of the isotopic composition of CO2 (13C/12C and 18O/16O), as well as O2/N2 and Ar/N2 are performed.
The continuous data from the BIK tall tower are published through the ICOS portal while the flask data are included in the BGC flask network release.
